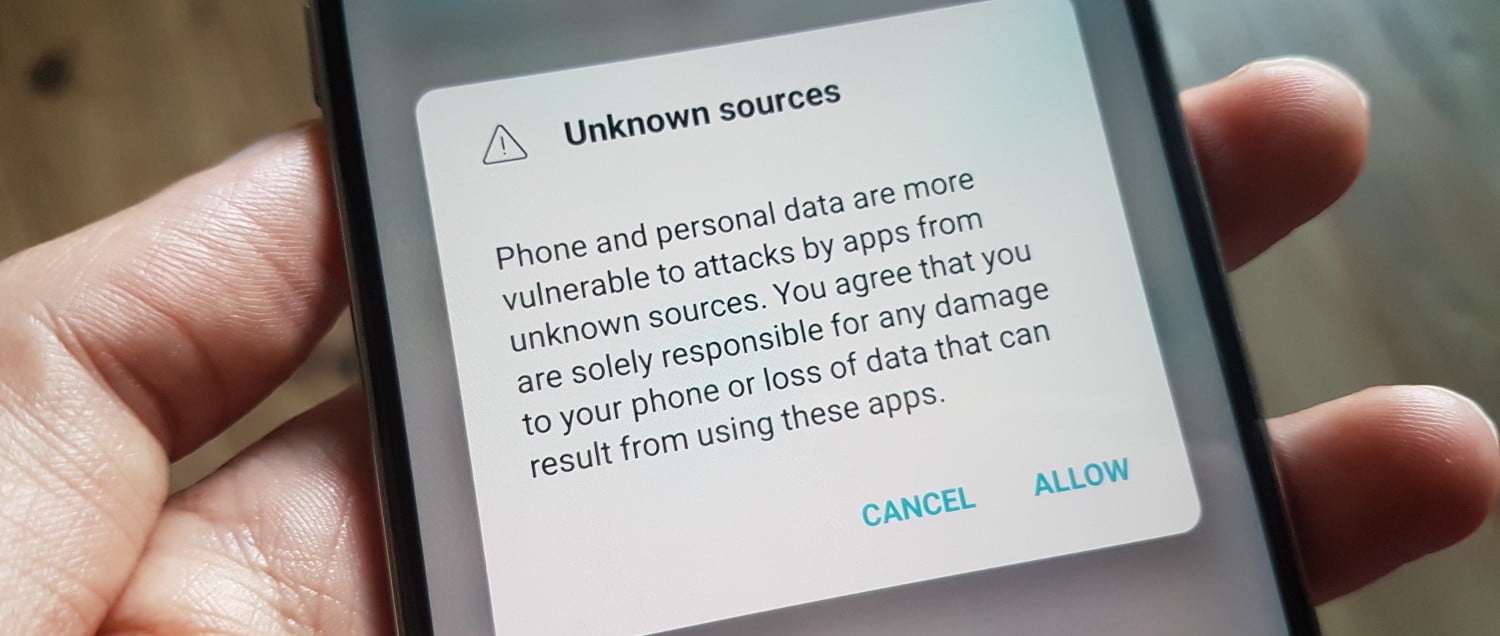
What is Unknown Sources?
Unknown sources define places outside the Google Play Store from which you downloaded an apk app. Google considers its own Play Store as the only trusted source for apps to be installed on Android.
However there are situations when you need to download unknown sources, such as apps coming from third-party marketplaces or apps that are currently in beta-testing phase. Platforms such as Appaloosa enable app distribution outside the Play Store and require such permissions. Such distribution method is also known as sideloading.
Since the early Android operating system versions, users have to explicitly approve unknown sources to be enabled in settings.
So if you are trying to install a downloaded apk without this setting enabled, you will be prompted with this message:
For your security, your phone is not allowed to install unknown apps from this source.

How to enable Unknown Sources in Android?
To allow apps to be downloaded from Unknown Sources, follow the steps below
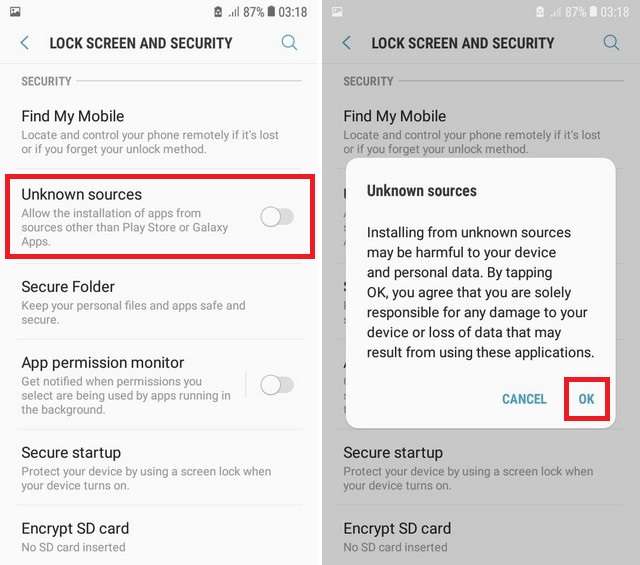
For old Android versions (4.0, Lollipop 5.0, Marshmallow 6.0, Nougat 7.0)
- Go to your Android Settings > Security
- Check the option Unknown sources
- Tap OK on the prompt message
- Select Trust
If you are running Android 9.0 and later, you will need to allow Unknown sources for each app willing to install an apk file. For instance if you are using two browsers such as Chrome and Firefox, you will need to allow both Chrome and Firefox to install unknown sources.
For New Android Versions (Oreo, Pie, Android 10, 11 and 12)
- Go to your Android Settings > Apps & Notifications
- Select Advanced or the three dots at the top-right corner – users might see either option depending on their device
- Select Special App Access
- Choose Install Unknown Apps
- Select the apps you want to allow to sideload apk files
About Security
As a good security measure, it is recommended that you don’t trust the source where you are installing the apps from. This restriction was introduced by Google to prevent malware from being distributed. As Google can only guarantee that apps originating from its own Google Play Store are safe, you should only activate unknown sources:
- from sources – ie developers or websites – that are trusted
- once when installing the app. You can deactivate this unknown sources feature after each use.
However you are still protected. Google has enabled a security feature on all Android phones called Google Play Protect. It aims at protecting the entire device with three features: theft prevention, web browsing protection and apps scanning. While it is generally activated on all devices, you can check its status in Google Play Store > Play Protect.
Apps scanning means that Google scans not only publicly available apk through their search engine, it also scan apps that are sideloaded by users on their device. This feature enables threat detection across devices. For instance if you are trying to download an apk file flagged as dangerous by Google Play Protect (either by their routine scanning or because other users have reported the file), it will display a warning message.
This means that even if you activate unknown sources, there’s still a safety net.
Unknown sources in an enterprise context
While unknown sources is commonly used to sideload apps for the general audience, businesses might also be interested in deploying apps outside the Google Play Store for their own employees or partners.
Businesses are then faced with two options for app distribution on Android:
- ask users to enable unknown sources for app installs only originating from an enterprise app store
- deploy a mobile application management solution making use of Google Play for Work
Enterprise app distribution with unknown sources
When allowing distribution of enterprise apps with unknown sources, admins either accept the risk associated with the policy or can’t do otherwise.
Indeed, if the target devices are already managed elsewhere by enterprise mobility management and if the app can’t be included into this solution, then there is no other option than apps sideloading.
However while users are afraid of risks using unknown sources, businesses should also be aware that using app sideloading does not offer protection to their app once installed and might expose it to tempering, hacking or theft.
Businesses in this scenario must protect their apps before its distribution or built their own safety need with app security development best practices.
Appaloosa offers a simple app store which can fit this app distribution use case.
Enterprise app distribution with mobile application management
There’s a better way to distribute apps in an enterprise context: mobile application management with Android Enterprise.
Mobile application management on Android enables the safe hosting and distribution of android apps to employees. When platforms such as Appaloosa make use of Google Play’s API, apps can be safely distributed without using unknown sources. They are hosted in a private, business section of the Google Play store and are kept in a secure, separate container on the user’s device.
